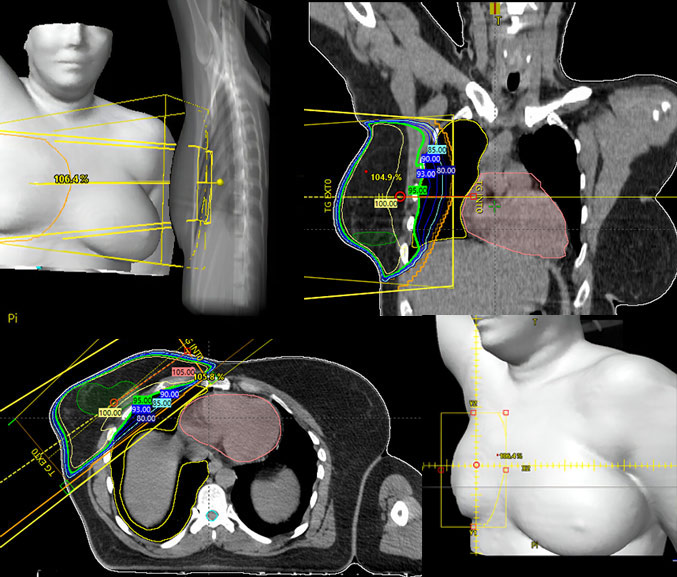
3D conformational processing
It relies on the use of patient images obtained by a CT scan in the same position in which the treatment will be carried out. The obtained images are reconstructed in three dimensions (3D). Powerful computers simulate the treatment by proposing the appropriate combination of beams for each location and by introducing the doses prescribed by doctors to achieve the appropriate treatment for the patient. These computers, equipped with the associated software suite known as treatment planning systems, perform complex algorithms to calculate the dosimetric distribution represented in three dimensions on the computer screens.
The result is what is called the “dosimetric report,” which includes, among other things, the setup parameters of the treatment units, as well as the doses in the various organs at risk and the monitor units (MU) that the device must deliver to carry out the treatment.